8 Things to Know About Renewable Energy Integration with Industrial Systems
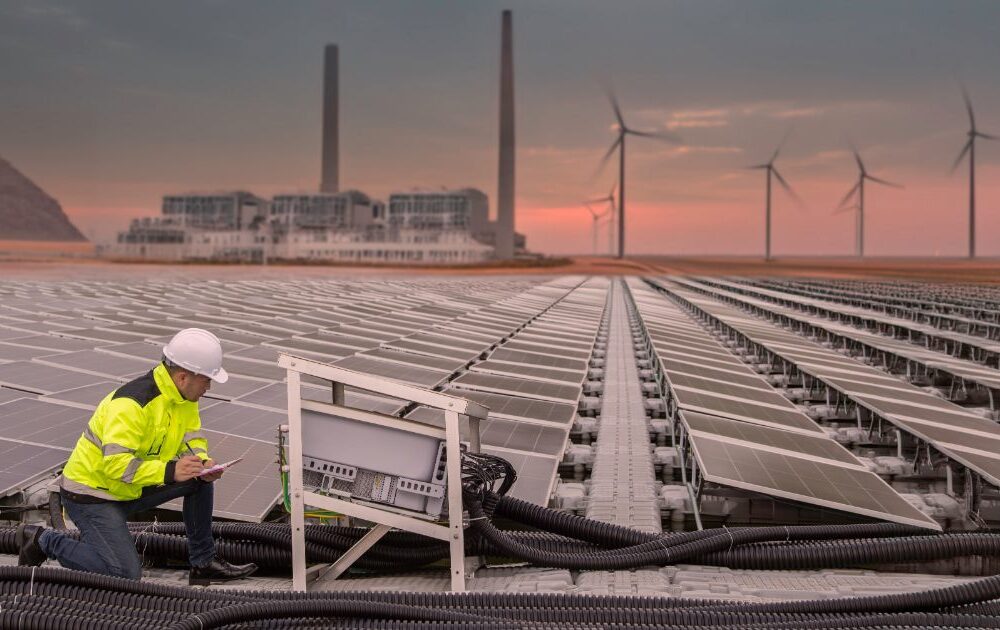
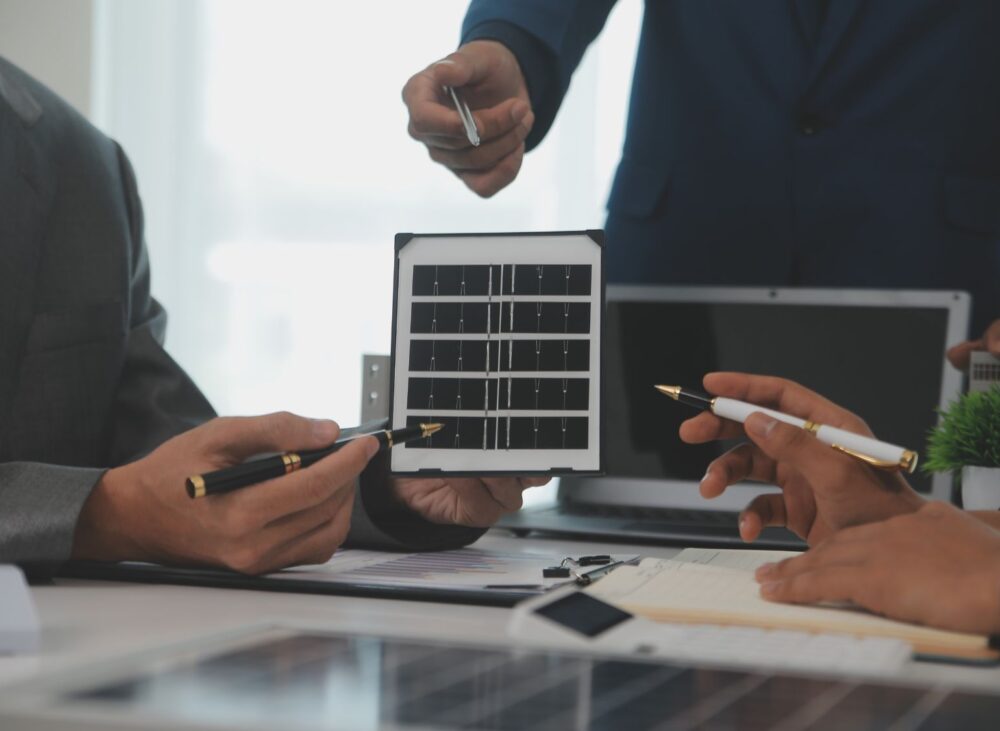
What’s New in Renewable Energy Integration: The renewable energy integration landscape has transformed significantly through 2024 and 2025. Global investment in solar photovoltaic reached USD 500 billion in 2024, surpassing all other generation sources for the first time. Battery storage investment grew by more than 20% and exceeded USD 50 billion, while the cost of lithium-ion batteries dropped 40% in 2024 alone following a 90% reduction over the previous decade. In the UAE, DEWA’s Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park reached 2,860 MW of commissioned capacity by the end of 2024, with plans to reach 5,000 MW by 2030. The Shams Dubai initiative continues expanding rooftop solar across commercial and industrial facilities, while the Hatta pumped-storage hydroelectric project nears completion as the first facility of its kind in the GCC region. For UAE industrial facilities, these developments create unprecedented opportunities for renewable energy integration that reduces operating costs while meeting sustainability objectives. Author Credentials: This guide is prepared by 3Phase Tech Services’ power systems engineering team with extensive experience implementing renewable energy integration projects across UAE industrial facilities. Our engineers hold certifications in power systems design, solar PV installation, and energy management systems. Through completed projects spanning manufacturing, water treatment, and commercial facilities, our team provides practical guidance based on real-world implementation experience in the regional operating environment. Scope of Technical Advice: This article provides technical guidance on renewable energy integration for industrial facilities as of January 2026. Specific implementation requirements vary based on facility load profiles, existing electrical infrastructure, and regulatory requirements. For tailored technical assessment of your facility’s renewable energy integration requirements, consultation with qualified engineering specialists is recommended. This guide does not substitute for professional engineering assessment, utility coordination, or equipment-specific manufacturer recommendations. 1. Understanding the Business Case for Industrial Renewable Energy Renewable energy integration for industrial facilities has evolved from an environmental initiative to a strategic business decision. UAE industrial facilities face unique opportunities that make renewable energy integration particularly attractive, combining high solar irradiance with supportive regulatory frameworks and declining technology costs. Economic Drivers for Industrial Renewable Energy The economics of renewable energy integration have shifted dramatically. Solar electricity costs in the UAE reached approximately 1.69 cents per kilowatt-hour in 2024, compared to 11 cents a decade earlier. This reduction makes solar generation competitive with or cheaper than grid electricity for many industrial applications. Industrial facilities typically operate during daylight hours when solar generation peaks, creating natural alignment between renewable generation and consumption patterns. Manufacturing operations with consistent daytime loads achieve high self-consumption rates, maximizing value by avoiding grid electricity purchases during peak production hours. Energy cost stability represents another driver. Industrial facilities with variable processes face exposure to utility rate fluctuations and demand charges. Renewable energy integration, particularly combined with battery storage, provides hedging against price volatility and creates predictable energy costs supporting long-term business planning. Sustainability and Stakeholder Requirements Beyond economic benefits, renewable energy integration addresses growing stakeholder expectations for corporate sustainability. Customers, investors, and regulatory bodies increasingly evaluate organizations on environmental performance, with energy sourcing becoming a key sustainability metric. Industrial facilities serving international markets face pressure to demonstrate sustainable operations. Supply chain requirements from multinational customers often specify renewable energy targets or carbon intensity thresholds. Renewable energy integration enables UAE facilities to meet these requirements while maintaining competitive positioning. Actionable Takeaway Conduct an energy cost analysis for your facility comparing current grid electricity costs against projected renewable generation costs over a 10 to 20 year horizon. Identify your facility’s load profile to determine alignment between consumption patterns and solar generation availability. Document stakeholder sustainability requirements that could be addressed through renewable energy integration. Contact 3Phase for energy assessment to evaluate your facility’s renewable energy potential. 2. Solar PV Systems for Industrial Facilities Solar photovoltaic systems represent the most widely deployed renewable energy integration technology for UAE industrial facilities. The region’s high solar irradiance, combined with mature technology and established installation capabilities, makes solar PV the foundation for most industrial renewable energy projects. System Configuration Options Industrial solar PV systems can be configured as rooftop installations, ground-mounted arrays, or carport structures depending on available space and facility requirements. Rooftop Systems utilize existing building surfaces to generate electricity without consuming additional land area. Industrial buildings with large flat roofs are particularly suitable for rooftop solar, with typical system sizes ranging from 100 kW to several megawatts depending on available roof area and structural capacity. The Shams Dubai program facilitates rooftop solar deployment for commercial and industrial facilities through streamlined permitting and net metering arrangements. Ground-Mounted Systems provide flexibility for larger installations where roof space is limited or structural constraints prevent rooftop deployment. Ground-mounted arrays can be oriented and tilted for optimal solar capture and are easier to maintain than rooftop systems. However, ground-mounted installations require dedicated land area and may not be suitable for facilities with limited site space. Carport Structures combine solar generation with vehicle shading, providing dual benefit for facilities with significant parking areas. Solar carports protect vehicles from UAE’s intense sun while generating electricity, though installation costs are higher than simple ground-mounted or rooftop systems. Sizing Considerations for Industrial Applications Proper system sizing balances generation capacity against facility consumption, grid export limitations, and investment requirements. Under DEWA’s Shams Dubai program, system capacity is capped based on customer connected load, with a maximum of 1,000 kW per plot. For industrial facilities, optimal sizing targets high self-consumption rates where generated electricity is consumed on-site rather than exported. Systems sized to match baseload consumption during solar production hours achieve highest value by offsetting grid electricity at retail rates. Load analysis forms the foundation for appropriate sizing. Facilities with consistent daytime operations may find solar generation closely matches consumption. Facilities with variable or shift-based operations may require battery storage for high self-consumption rates. System Type Typical Size Range Best Application Rooftop 100 kW to 2 MW Industrial buildings with large flat roofs Ground-Mounted 500 kW to 10+ MW Facilities with available land area Carport 50 kW to 500 kW Facilities with significant